A flexible printed circuit connects electronic components using conductive pathways on a bendable substrate. You experience a major advantage when you use flexible printed circuits: flexibility enables circuits to flex, twist, and fold without damage. Unlike rigid boards, flexible circuits adapt to tight spaces and withstand repeated flex cycles. Flexibility drives innovation in flexible electronics, allowing devices to fit curved surfaces and endure mechanical stress. Manufacturers invest in flexible printed circuit technology because it supports compact designs and reliable performance. The global market for flexible printed circuit boards is expanding rapidly, with a projected 13.7% CAGR from 2025 to 2030, outpacing rigid circuit boards.
| Type of Circuit Board | Market Size (2024) | Projected Market Size (2030) | CAGR (2025-2030) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flexible Printed Circuit Boards | USD 23.89 billion | USD 50.90 billion | 13.7% |
| Rigid Printed Circuit Boards | N/A | N/A | 6.3% |
You gain practical answers about structure, function, benefits, and uses by understanding how flexibility shapes the future of electronics.
Key Takeaways
- Flexible printed circuits adapt to tight spaces and withstand bending, making them ideal for modern electronics like wearables and smartphones.
- Using materials like polyimide and PEEK enhances durability and performance, ensuring reliable operation in harsh environments.
- Flexible circuits reduce the size and weight of devices, allowing for innovative designs without compromising functionality.
- These circuits excel in applications requiring frequent movement, absorbing vibrations and maintaining electrical integrity over time.
- Investing in flexible printed circuit technology supports sustainability by minimizing waste and reducing the use of harmful chemicals.
Flexible Printed Circuit Basics
What Is a Flexible Printed Circuit
You encounter flexible printed circuits in many modern electronic devices. A flexible printed circuit uses thin, bendable materials to connect electronic components. Unlike traditional rigid boards, a flexible printed circuit board can twist, fold, and adapt to tight spaces. This adaptability comes from the use of specialized materials and advanced manufacturing techniques.
Flexible printed circuit boards rely on substrates like polyimide, polyester, or liquid crystal polymer. Polyimide stands out for its high temperature resistance and tensile strength, making it ideal for demanding environments. Polyester offers a cost-effective solution for less extreme conditions, while liquid crystal polymer provides excellent dimensional stability and low moisture absorption. These materials allow flexible circuit boards to maintain performance even when exposed to heat, cold, or mechanical stress.
You can see the differences between rigid and flexible circuit board design in the table below:
| Feature | Rigid PCBs | Flexible PCBs |
|---|---|---|
| Base Material | Non-conductive substrate, usually fiberglass | Flexible materials like polyimide |
| Flexibility | Strong and rigid | Can bend and fold into various shapes |
| Conductors | Electro-deposited copper | Rolled annealed copper for flexibility |
| Manufacturing Process | Uses a solder mask layer | Uses coverlays to protect exposed circuits |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | More expensive but adaptable to compact spaces |
| Durability | Higher strength | Absorbs vibrations and withstands bending cycles |
| Weight | Heavier due to thickness | Lighter, suitable for smaller components |
| Resistance | More susceptible to damage from heat | Better resistance to high temperatures |
| Design Complexity | Suitable for basic devices | Ideal for compact and innovative products |
You benefit from flexible circuit board design when you need lightweight, thin, and reliable connections in compact devices. Flexible circuits excel in environments where space is limited and mechanical movement is frequent.
Key Features and Flexibility
You gain several advantages when you use flexible printed circuit boards. The most important feature is their ability to flex and adapt to different shapes. This flexibility allows you to design products that fit into small or irregular spaces, such as wearable devices, foldable phones, or medical sensors.
Tip: Flexible circuit board design lets you create products that are lighter and more durable than those using rigid boards.
Key principles of flexible circuit board design focus on maximizing reliability and lifespan. You must consider the bend radius, which is the minimum radius you can bend the circuit without causing damage. A larger bend radius reduces stress on copper conductors and extends the life of the circuit. For example, single-sided circuits require a bend radius of 3 to 6 times the circuit thickness, while dynamic applications may need 20 to 40 times the thickness.
| Circuit Type | Recommended Bend Radius (times circuit thickness) |
|---|---|
| Single-sided circuits | 3 to 6 times |
| Double-sided circuits | 6 to 10 times |
| Multilayer circuits | 10 to 15 times |
| Dynamic applications | 20 to 40 times |
You should also understand how flexural fatigue affects flexible pcb reliability. Repeated bending can cause microcracks in copper traces or separation between layers. Choosing rolled annealed copper and following proper design guidelines helps prevent these issues.
Flexible printed circuit boards offer several distinguishing features:
- Small body and lightweight construction
- High adaptability to different shapes and movements
- Cost-effective for complex, compact designs
- High reliability and excellent resistance to heat and dielectric breakdown
You will find that flex circuits can endure hundreds of thousands of flex cycles without failure. This makes them essential for applications that require frequent movement or exposure to harsh environments. Flexible circuits absorb vibrations and withstand temperature extremes better than rigid boards.
When you design with flexible circuit boards, you unlock new possibilities for innovation. You can create products that are not only smaller and lighter but also more reliable and durable. Flex pcbs support the demands of modern electronics, from consumer gadgets to advanced medical devices.
Flexible Printed Circuit Board Structure

Substrate Materials (Polyimide, PEEK)
You rely on the substrate as the foundation of any flexible pcb. Polyimide and PEEK stand out as the most widely used materials. Polyimide offers high temperature resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for demanding environments. PEEK provides superior mechanical durability and outstanding thermal stability, allowing your pcb to operate at temperatures up to 250°C. Both materials deliver excellent chemical resistance, which prolongs the life of your pcb in harsh conditions. You benefit from their low dielectric constant and high dielectric strength, ensuring reliable signal transmission and performance in high-voltage or telecommunications applications. PEEK also supports biocompatibility, which is essential for medical and wearable devices.
| Material | Thermal Properties | Mechanical Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Polyimide | High temperature resistance | Flexibility, lightweight |
| PEEK | Exceptional thermal stability | Superior durability, biocompatibility |
Tip: Choose polyimide for flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Select PEEK when you need maximum durability and chemical resistance.
Conductive Layers and Patterns
You find that the conductive layers in a flexible pcb use rolled annealed copper for optimal flexibility and conductivity. Manufacturers use photolithographic technology, such as Laser Direct Imaging (LDI), to create precise circuit patterns. LDI enables rapid design changes and prototyping, which streamlines production and reduces costs. You achieve fine features and complex patterns, making your pcb suitable for advanced electronics. The ability to bypass traditional masks with LDI increases throughput and shortens production cycles.
- LDI provides excellent precision for most flex pcb applications.
- You can implement rapid design changes without costly mask modifications.
- Fine features and complex patterns become possible, supporting innovative product designs.
Insulation and Protection
You protect your flexible pcb from environmental hazards using advanced insulation materials. Epoxy resins offer excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength. Polyimide films provide high flexibility and thermal stability, while liquid crystal polymer ensures superior moisture resistance. These materials shield your pcb from moisture, dust, and temperature fluctuations, maintaining functionality over time.
To reinforce your pcb in harsh environments, you use several protection methods:
- Stiffeners strengthen specific areas, reducing stress on solder joints and connectors.
- Strain relief fillets apply flexible adhesive at transitions to mitigate stress concentrations.
- Proper bend radius prevents excessive stress and extends the lifespan of your pcb.
Note: The choice of insulation and protection methods directly impacts the reliability and longevity of your flexible pcb, especially in automotive, medical, and industrial applications.
How Flexible Circuits Work
Electrical Function
You rely on flexible printed circuits to transmit electrical signals efficiently in compact and dynamic environments. The core structure uses copper foil as the conductive layer, which sits on a flexible insulating substrate such as polyimide film. This combination allows you to create intricate circuit patterns that maintain high reliability even when bent or twisted. Flexible printed circuits often feature multiple layers, using through holes and vias to interconnect components and increase circuit density. You benefit from this design when you need to fit electronics into tight spaces or curved surfaces.
Flexible pcbs deliver outstanding electrical performance. You achieve low electrical resistance and high dielectric strength, which ensures stable signal transmission and minimizes energy loss. The table below highlights typical electrical properties:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | 6000 V/mil |
| Volume Resistivity | 1.0E+16 ohm-cm |
You find that flex circuit boards can withstand millions of flex cycles without compromising electrical integrity. Unlike traditional rigid boards, flexible circuits maintain consistent performance even under repeated mechanical stress. You can optimize flex pcb performance by selecting high-quality materials and precise manufacturing techniques.
- Flexible printed circuits use copper foil and polyimide for flexibility and reliability.
- Flex pcbs support high circuit density with multilayer designs.
- You achieve stable electrical signals and low resistance.
Mechanical Flexibility
You experience the true advantage of flexible circuits in their mechanical properties. Flex pcbs endure vibrations, shocks, and repeated bending, making them ideal for rugged and mobile applications. The table below summarizes the mechanical stresses these circuits handle:
| Mechanical Stress | Description |
|---|---|
| Vibrations | Flexible pcbs can endure vibrations, making them suitable for dynamic environments. |
| Shocks | They are designed to withstand shocks, ensuring reliability in rugged applications. |
| Bending | Their flexibility allows them to be bent without damage, crucial for compact designs. |
You gain additional benefits from thermal stability, tensile strength, and flexibility. Flex circuits resist stretching and tearing, which allows you to design innovative products without worrying about damage during use. You can bend, fold, and wind flexible pcb assemblies to fit unique shapes and spaces.
- Flex pcbs absorb vibrations and shocks, protecting sensitive components.
- You can bend flex circuits repeatedly without causing microcracks or failures.
- Flexible pcb materials maintain performance in high-temperature environments.
Tip: When you design with flexible printed circuit technology, you unlock new possibilities for compact, durable, and reliable electronics.
You see flexible printed circuits in wearable devices, automotive systems, and medical equipment. Their ability to flex and adapt to movement ensures long-term reliability and supports advanced product designs.
Advantages and Limitations
Benefits of Flexible Circuits
You gain significant advantages when you choose flexible printed circuit boards for your electronic designs. Flexible circuits adapt to complex shapes and tight spaces, which is essential for modern devices like wearables and IoT sensors. You can reduce the size and weight of your products because flex pcbs occupy only about 10% of the space and weight of traditional pcb assemblies. This miniaturization enables you to create lighter, more portable devices.
Flex circuit boards allow you to route ultra-narrow lines and spaces, supporting high-density device populations. You can design products with more features without increasing bulk. Cleaner manufacturing processes for flexible printed circuits also help you reduce waste and minimize the use of harmful chemicals, supporting sustainability goals.
Tip: You improve reliability in environments with vibration and mechanical stress by using flex circuits, which withstand repetitive bending and flex cycles.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Adaptability | Flex circuits bend and fit into irregular spaces, ideal for compact designs. |
| Space Efficiency | Flex pcbs reduce weight and size, streamlining packaging. |
| Reliability | Flexible printed circuits perform well under vibration and stress. |
| Cost Reduction | Fewer wiring errors and simplified assembly lower costs. |
| Durability | Flex circuit boards last longer, reducing electronic waste. |
You also benefit from reduced human error during wiring and improved thermal management. Cleaner manufacturing and fewer materials lead to cost savings and a lower carbon footprint.
- Flexible printed circuit boards integrate into products with complex form factors.
- You use fewer materials, saving costs and supporting eco-friendly manufacturing.
- Flex pcbs enable compact, lightweight, and feature-rich designs.
Common Drawbacks
You must consider several limitations when working with flexible pcb technology. The materials for flexible printed circuits cost up to ten times more than those for rigid boards. Manufacturing processes require ultra-thin materials, which increases complexity and production costs. Mishandling ZIF connectors can cause cracks in contacts, and sharp bends at rigid-to-flex transitions may damage the pcb.
Excessive heat during component replacement can lift or tear pads, leading to failures. You need to pay close attention to proper handling and design guidelines to avoid these issues.
- Mishandling connectors may result in contact cracks.
- Sharp bends at rigid-to-flex transitions can damage the pcb.
- Excessive heat during repairs can lift or tear pads.
- Flexible pcb materials and manufacturing are more expensive than rigid boards.
- You must follow strict design rules to prevent failures in flex circuits.
Note: Rigid-flex pcb designs can offer long-term savings by reducing the number of components and simplifying assembly, but initial costs remain higher.
You should weigh the benefits of flexible printed circuit boards against these drawbacks to determine the best solution for your application.
Applications of Flexible Printed Circuits

Consumer Electronics
You see flexible printed circuit boards driving innovation in consumer electronics. Flex pcbs enable sleek, lightweight designs for smartphones, tablets, and wearables. You can integrate flex circuit boards into foldable displays, smart clothing, and compact gadgets. These circuits bend to a radius of less than 5 mm or stretch up to 30% without failure, supporting dynamic flex pcb applications. You benefit from ultra-thin, adaptable circuits that fit into tight spaces and allow for new product shapes. The demand for smaller, lighter devices pushes manufacturers to rely on flex technology for advanced form factors.
- Flex circuits support foldable phones and tablets.
- You find flex pcbs in smartwatches and fitness trackers.
- Flexible circuits replace rigid boards in low-powered devices, expanding design possibilities.
Medical Devices
You rely on flex pcbs for critical medical technology. Flexible circuits power heart monitors in smartwatches, implantable devices like pacemakers and neurostimulators, and portable diagnostic tools. You see dynamic flex pcb applications in surgical instruments and robotic-assisted surgery systems. Flexible sensors for patient monitoring, such as ECG and temperature sensors, use flex to conform to the body and deliver accurate readings.
| Evidence Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Compact Design | Flexible printed circuit boards reduce device size and weight, improving portability. |
| Reduced Component Failure | Flex circuits minimize moving parts, lowering the risk of malfunction. |
| Compliance with Standards | Manufacturing meets strict medical standards, ensuring patient safety. |
You gain reliability and safety in medical devices by using flex circuits that withstand repeated movement and harsh conditions.
Automotive and Industrial Uses
You encounter applications of flex circuit boards in modern vehicles and industrial automation. Automotive systems use flex pcbs for infotainment screens, sensors, lighting, battery management, and safety features. These circuits connect components in tight spaces and enable sleek LED designs. You benefit from dynamic flex pcb applications that absorb vibration and withstand repeated motion.
| Application Area | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Infotainment Systems | Flex connects screens and speakers, allowing flexible design. |
| Sensors | Flex pcbs measure parameters in tight spaces, improving reliability. |
| Lighting | Flex enables compact LED systems, optimizing space and aesthetics. |
In industrial automation and robotics, you use flex circuits for adaptability, durability, and space optimization. Flex pcbs conform to robotic shapes, absorb stress, and reduce wiring needs. You achieve reliable, repeatable performance in robots and automated systems.
- Flex circuits enhance reliability by reducing connectors and wiring.
- You optimize space and weight in robotic assemblies.
- Flex pcbs withstand repetitive motions in dynamic flex pcb applications.
You see flexible circuits transforming industries by enabling compact, reliable, and innovative designs across consumer, medical, automotive, and industrial sectors.
You see how flex circuits transform electronic design by combining flexible substrates, copper traces, and advanced assembly techniques. Flex enables devices to bend, fit into compact spaces, and withstand harsh environments. You benefit from reduced weight, improved reliability, and versatile applications in consumer electronics, automotive, and medical fields. Flex supports innovation in wearable technology and medical monitoring. If you want to explore how flex can optimize your next project, contact our team for expert guidance and resources.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of using flex circuits in electronics?
You gain the ability to design devices that bend, fold, and fit into compact spaces. Flex circuits support lightweight, durable products. You see them in wearables, medical sensors, and automotive systems. For more details, you can contact our team through the website.
How do flex circuits improve reliability in harsh environments?
You benefit from flex circuits because they absorb vibrations and withstand repeated bending. Polyimide and PEEK substrates resist heat and chemicals. Flex circuits maintain performance in automotive, industrial, and medical applications. You can ask further questions using our contact form.
Can you repair or modify a flex circuit after installation?
You can repair flex circuits, but you must use specialized tools and techniques. Excessive heat or sharp bends may damage the circuit. For guidance on safe repairs, you should reach out to our technical support team.
Where can you find academic references about flex circuit technology?
You can review IEEE Xplore and the Journal of Electronic Materials for research on flex circuit design and materials. Books like "Flexible Electronics: Materials and Applications" by Wong and Salleo provide in-depth information. If you need more resources, please send us a message.
How do you choose the right flex circuit for your project?
You select a flex circuit based on temperature, mechanical stress, and space requirements. Polyimide suits high-flex applications. PEEK works for extreme durability. For personalized recommendations, you can contact our experts through the website.










 2025-12-05
2025-12-05
 BEST
BEST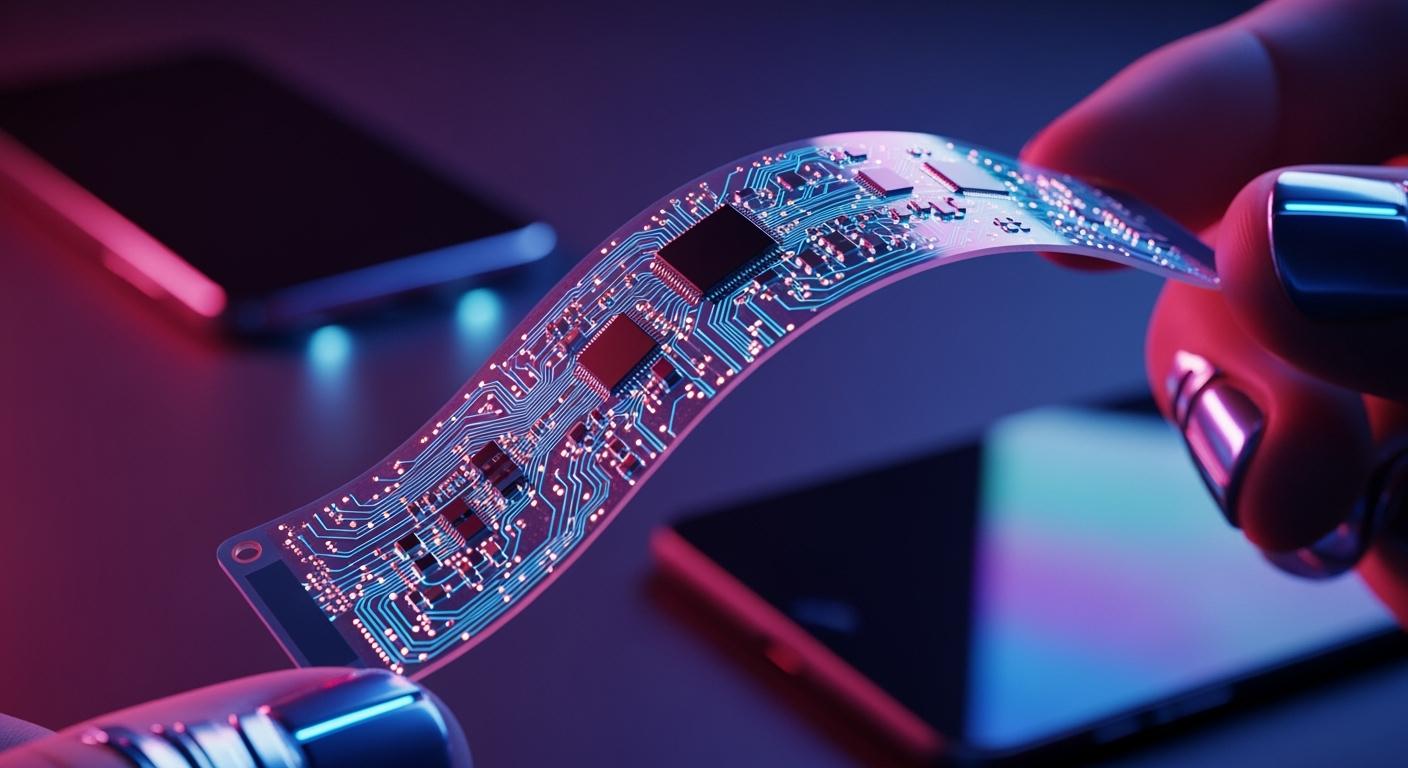


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)

